Ingress to applications managed by Rancher in Kubernetes
To use the ngrok Kubernetes Operator with Rancher in a local cluster:
The ngrok Operator for Kubernetes is the official controller for adding secure public ingress and middleware execution to your Kubernetes applications with ngrok's Cloud Edge. With ngrok, you can manage and secure traffic to your applications at every stage of the development lifecycle while also benefitting from simpler configurations, security, and edge acceleration.
Rancher is an open source multi-cluster orchestration management platform developed by SUSE. DevOps teams use Rancher to make their multi-cluster and -cloud environments more efficient, secure, and resilient, which in turn provides a better developer experience for developers building and deploying cloud native applications.
The ngrok Kubernetes Operator and Rancher integrate to overcome Kubernetes complexity and improve collaboration through the creation of an internal developer platform (IDP) or enabling developers to focus on building, not configuring, their applications.
With this guide, you'll launch Rancher's management platform, create a new RKE2 cluster, connect your cluster's ingress to ngrok using Rancher's Chart repository, and deploy a demo application, which will then be reachable to public traffic.
- An ngrok account.
- One or more Linux hosts that meet Rancher's requirements for operating as Kubernetes nodes. Your hosts can be local/on-prem virtual machines, cloud-based virtual machines, or bare metal servers.
- Docker installed locally.
- kubectl installed locally.
Step 1: Install Rancher via Docker
To follow along with this guide, you need Rancher installed on a local or remote Kubernetes cluster. If you already have an existing cluster running Rancher, you can skip this step and proceed to Step 2: Install the ngrok Ingress Controller.
In the following steps, you'll run Rancher, and create the Kubernetes cluster it runs on, within a Docker container. This simple, local-only installation option should be used only for test and demonstration purposes. You can, however, use the Rancher backup operator to migrate this Docker container-based installation to a production-ready, high-availability Kubernetes cluster.
The following steps also assume you have already provisioned one or more Linux hosts that will operate as nodes for the new Kubernetes cluster managed by Rancher.
Another viable option is to launch a single Linux virtual machine on your local workstation or with a cloud provider to host a K3s cluster for installing Rancher with Helm. If you choose that option, you can skip ahead to Step 2: Install the ngrok Ingress Controller once you’ve finalized your K3s cluster.
- Launch the Rancher server in a detached, privileged Docker container. With this configuration, you'll access Rancher on
localhostusing a specific port.
docker run --privileged --restart=unless-stopped -d -p 81:80 -p 444:443 rancher/rancher:latest
- Once Docker finishes running, check to ensure your Rancher container is running properly.
docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
d43eceb2e5b2 rancher/rancher:latest "entrypoint.sh" About a minute ago Up About a minute 0.0.0.0:81->80/tcp, :::81->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:444->443/tcp, :::444->443/tcp vigilant_clarke
- Navigate to
https://localhost:444in your browser, which will warn you about self-signed SSL certificates. Pass through that warning, which will show you a prompt from Rancher asking for your bootstrap password, which you need to initialize Rancher. Copy and paste that command into your terminal, replacing[DOCKER_NAME]with the name output usingdocker ps.
docker logs [DOCKER_NAME] 2>&1 | grep "Bootstrap Password:"
-
Copy the terminal output into the password input and click Log in with Local User. Next, choose between a randomly-generated password or one of your choosing to initialize the admin user.
-
The Server URL field will default to
https://localhost:444, but your worker nodes won't be able to connect to Rancher in this configuration. Find your local IP address—tryhostname -Ifor Linux oripconfig getifaddr en0on macOs—which will look similar to192.168.1.123, and replacelocalhostwith it, similar to the following:https://192.168.1.107:444.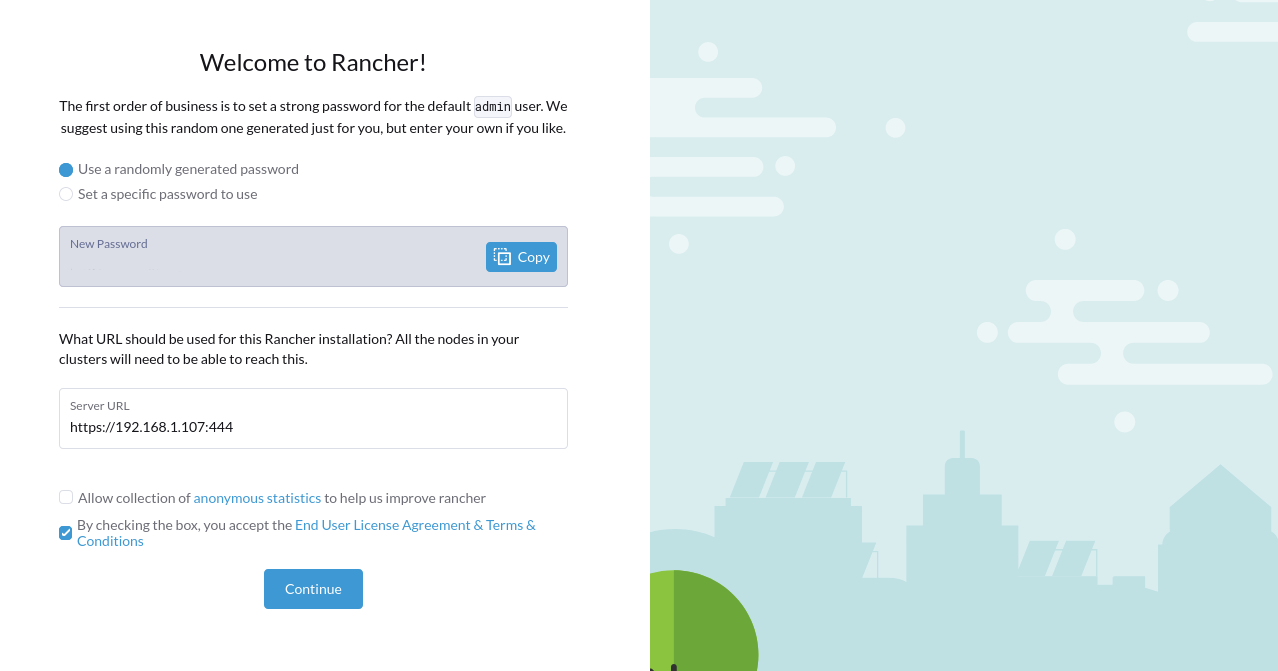
When the Rancher dashboard loads, Rancher should have already deployed a single K3s-based cluster named
local—click on the cluster's name to explore. Rancher recommends that its server management and your workloads run on separate clusters, which is what you'll do next. -
Create a new RKE2 cluster by clicking Create in your Rancher dashboard home, then Custom to deploy a custom cluster. Give your cluster a name, and under the System Services heading, uncheck NGINX Ingress, as you'll add ngrok-based ingress in the next step. Click Create to initialize the cluster.
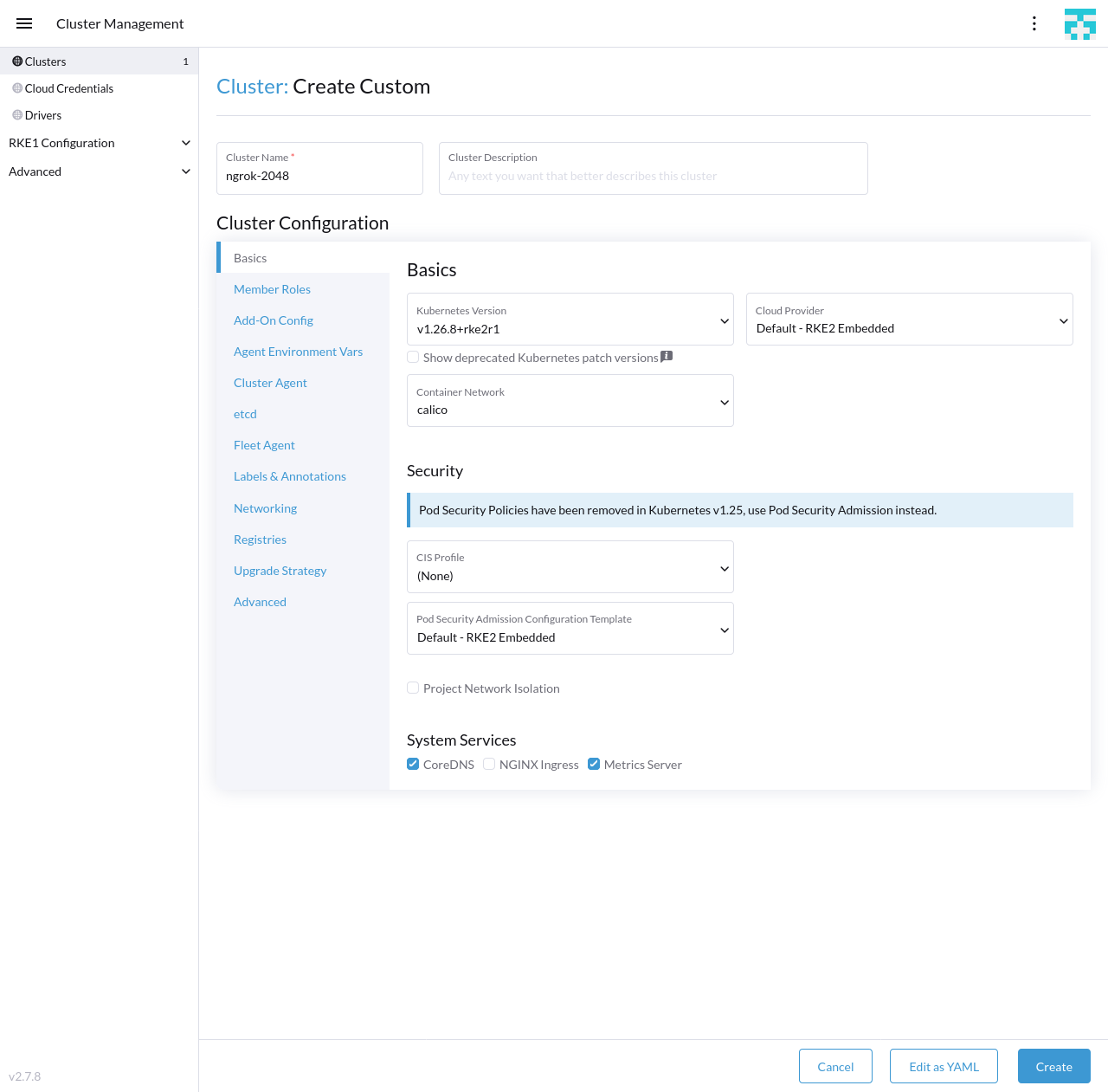
-
Register your Linux node(s) with your RKE2 cluster. Leave the Node Role options at their defaults, and under the Registration Command heading and command example, click the Insecure checkbox.
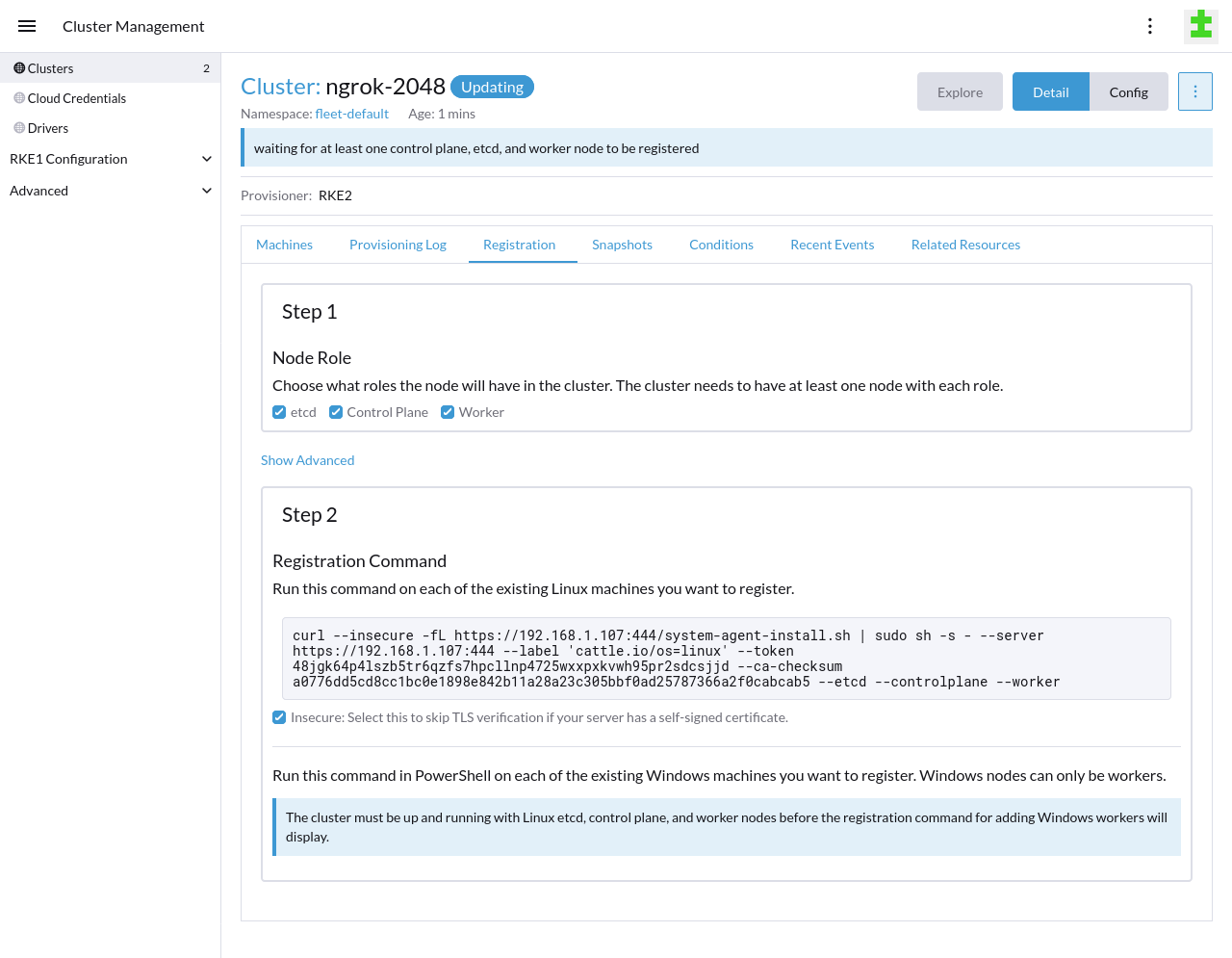
Once you copy-paste the command into your Linux node and execute it, your new cluster will begin bootstrapping the node. When Rancher finishes bootstrapping your node(s), you can navigate to the Cluster Dashboard for your RKE2 cluster, explore deployed resources, and see basic usage metrics.
-
Set up
kubectlto manage your RKE2 cluster. At the top of the Cluster Dashboard, click the Copy KubeConfig to Clipboard option.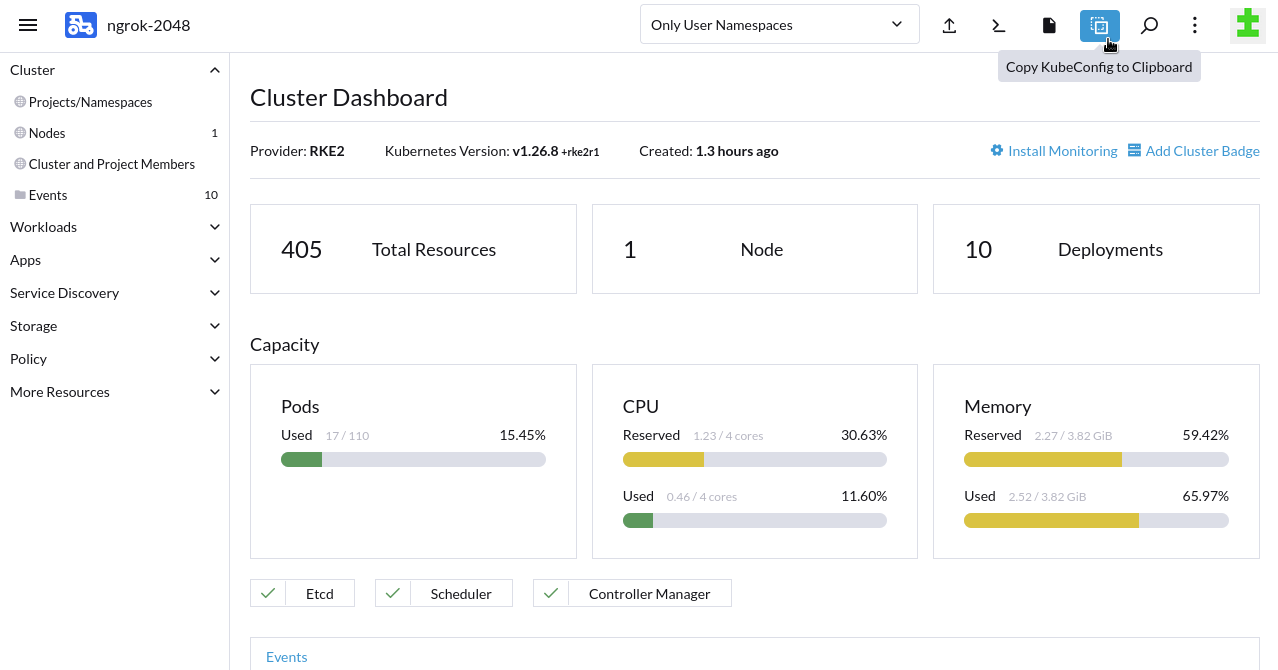
Paste the content of your clipboard into your
~/.kube/configfile. -
Ensure your new RKE2 cluster is active by getting the namespaces for your instance. Your list of namespaces should look like the following:
kubectl get namespaces
NAME STATUS AGE
calico-system Active 4m
cattle-impersonation-system Active 29s
cattle-system Active 5m
default Active 5m4s
kube-node-lease Active 5m6s
kube-public Active 5m6s
kube-system Active 5m6s
local Active 23s
tigera-operator Active 4m10s
You have now installed Rancher in a Docker container, created a new Kubernetes cluster for your applications, and connected one or more Linux nodes to Rancher for handling future workloads.
Step 2: Install the ngrok Kubernetes Operator using Rancher
Next, install the ngrok Kubernetes Operator, which will then automatically handle public ingress to any properly configured application you add to your cluster. Because this guide focuses on integrating Rancher's management tool with Kubernetes ingress, the following steps will show how to add the ngrok Kubernetes Operator via the Rancher dashboard.
You can also install the ngrok Kubernetes Operator with Helm instead of via Rancher's management platform. See our Using ngrok with Kubernetes guide for details.
-
Create an
ngrok-operatornamespace.kubectl create namespace ngrok-operator -
Get your ngrok
AUTHTOKENandAPI_KEYcredentials.Find your
AUTHTOKENunder Your Authtoken in the ngrok dashboard.To create a new API key, navigate to the API section of the ngrok dashboard, click the New API Key button, change the description or owner, and click the Add API Key button. Don't close the modal window yet, as you'll need this API key for the next step.
-
Create a Kubernetes Secret named
ngrok-operator-credentials, replacing[YOUR-AUTHTOKEN]and[YOUR_API_KEY]in the command below with your ngrok credentials. Rancher will use this secret to authenticate the ngrok Kubernetes Operator with your account.kubectl create secret generic --namespace ngrok-operator ngrok-operator-credentials \
--from-literal=AUTHTOKEN=[YOUR-AUTHTOKEN] \
--from-literal=API_KEY=[YOUR-API-KEY] -
Add the Helm Chart for the ngrok Kubernetes Operator via Rancher. From the Cluster Dashboard for your RKE2 cluster, click on Apps in the sidebar, then Charts. Search for
ngrok Kubernetes Operatorand click through to the README. Click Install to begin configuration.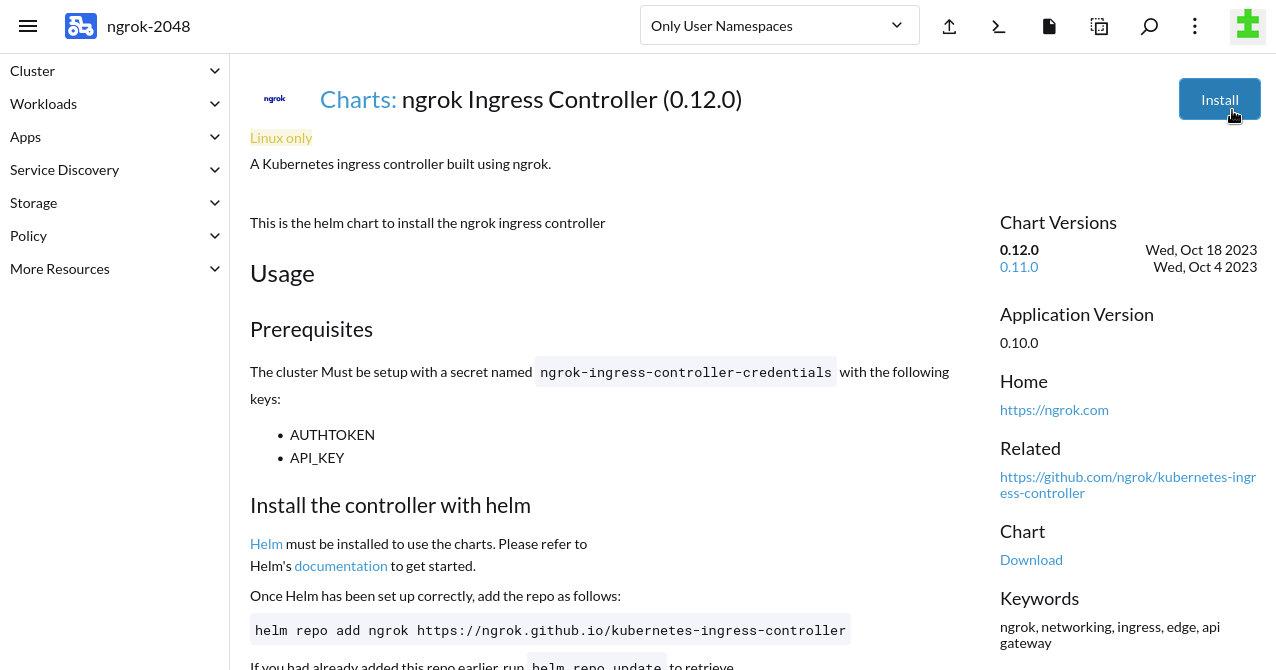
In the Metadata step, choose
ngrok-operatoras the namespace, then click Next.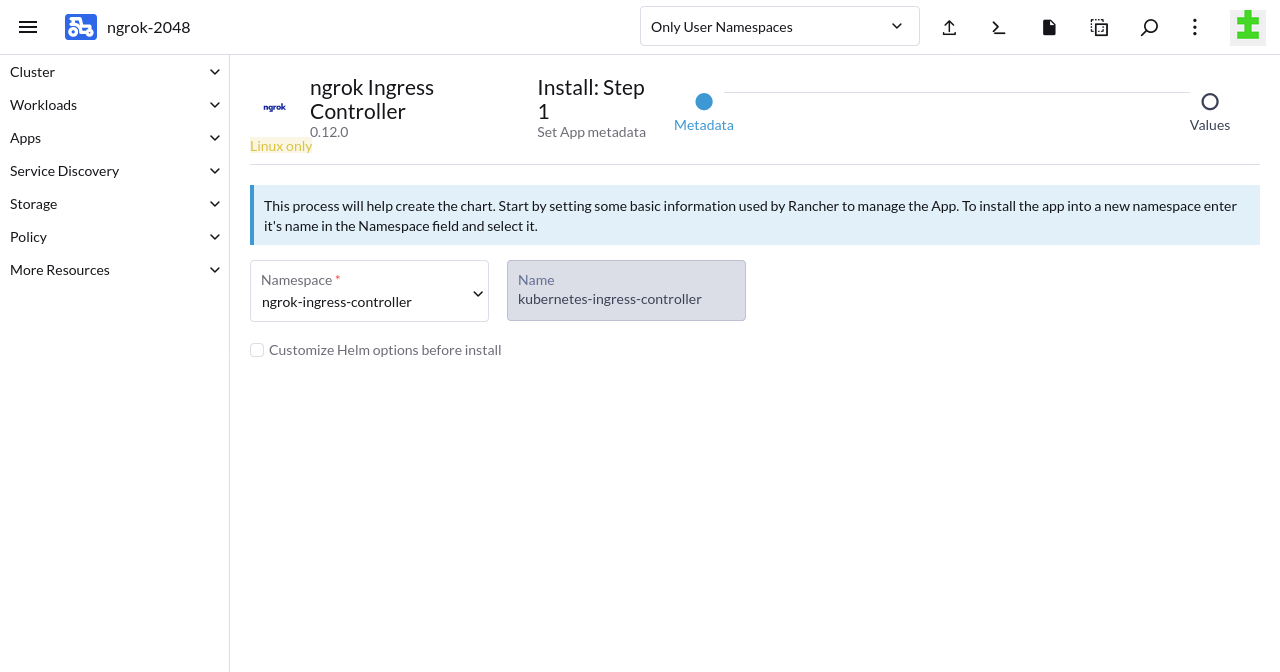
In the Values step, update the
credentialsportion of the default YAML to include thengrok-operator-credentialssecret you created previously.credentials:
apiKey: ""
authtoken: ""
secret:
name: "ngrok-operator-credentials"Click Install. Rancher will take a few moments to initialize the necessary resources, then show that the ngrok Operator deployed successfully.
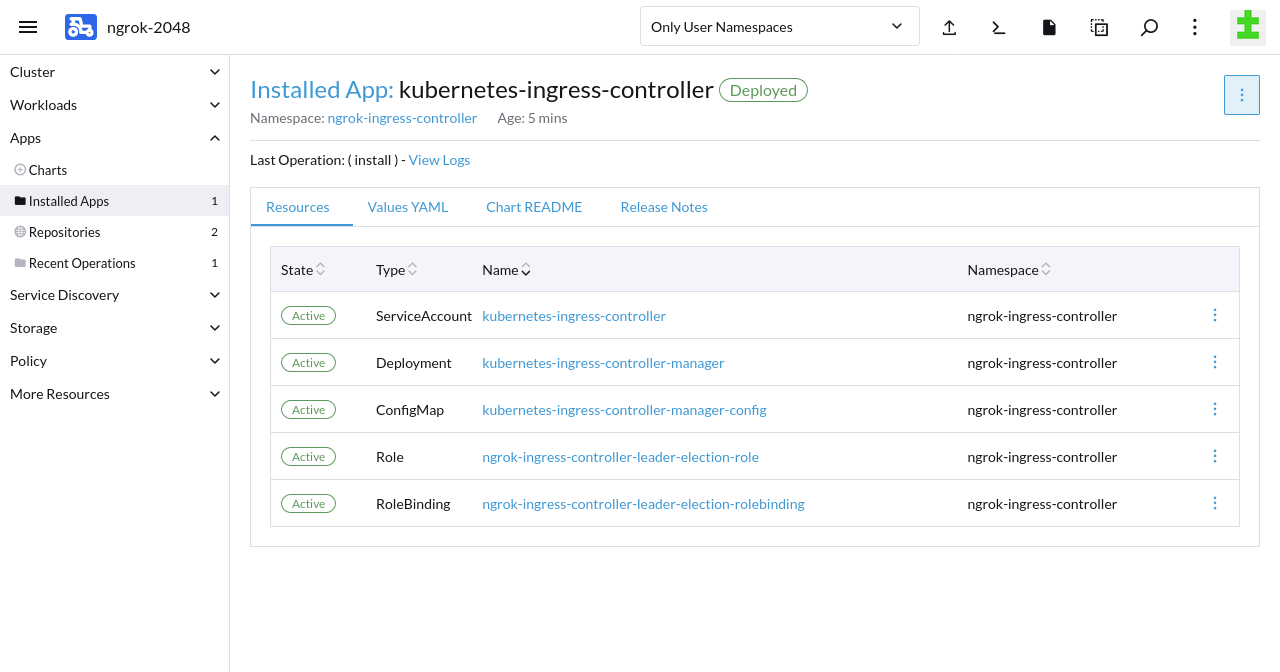
Step 3: Install a sample application
Now that you have the ngrok Kubernetes Operator running and authenticated with your credentials, you're ready to add a sample application to your cluster. The ngrok Kubernetes Operator will connect this application to the ngrok cloud edge, simplifying how you route external traffic through your Rancher-managed cluster.
-
Create a ngrok static subdomain for ingress if you don't have one already. Navigate to the Domains section of the ngrok dashboard and click Create Domain or New Domain. This static subdomain will be your
NGROK_DOMAINfor the remainder of this guide.Creating a subdomain on the ngrok network provides a public route to accept HTTP, HTTPS, and TLS traffic.
-
Create a new Kubernetes manifest (
2048.yaml) with the below contents. This manifest defines the 2048 application service and deployment, then configures the ngrok Kubernetes Operator to connect thegame-2048service to the ngrok edge via yourNGROK_DOMAIN.tipMake sure you edit line 45 of the manifest below, which contains the
NGROK_DOMAINvariable, with the ngrok subdomain you just created. It should look something likeone-two-three.ngrok.app.apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: game-2048
namespace: ngrok-operator
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: game-2048
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: game-2048
namespace: ngrok-operator
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: game-2048
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: game-2048
spec:
containers:
- name: backend
image: alexwhen/docker-2048
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
---
# ngrok Kubernetes Operator configuration
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: game-2048-ingress
namespace: ngrok-operator
spec:
ingressClassName: ngrok
rules:
- host: NGROK_DOMAIN
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: game-2048
port:
number: 80 -
Apply the
2048.yamlmanifest to your RKE2 cluster.kubectl apply -f 2048.yamltipNote: If you get an error when applying the manifest, double check that you've updated the
NGROK_DOMAINvalue and try again. -
Access your 2048 demo app by navigating to your ngrok subdomain, e.g.
https://one-two-three.ngrok.app. ngrok's edge and your Operator will route traffic to your app from any device or external network as long as your Rancher server and application cluster remain operational.
What's next?
You've now used the open source ngrok Kubernetes Operator to add public ingress to your Rancher-managed cluster and sample application without worrying about IPs, network interfaces, or VPC routing. Because ngrok offloads ingress and middleware execution to its global edge, you can follow a similar procedure for Rancher-managed clusters in any on-prem or cloud Kubernetes environment, like EKS, GKE, and more.
After deploying this proof-of-concept environment, you can take your integration between Rancher and the ngrok Ingress Controller in several directions.
Backup and/or migrate to a high-availability Rancher installation
Backups are always a good idea to prevent data loss, and are also the best way to convert your Docker-based installation of Rancher into a production-grade environment that leverages the ngrok cloud edge to handle ingress with no additional configuration.
- Back up your Rancher installation
using a sequence of
docker ...commands to create a data container and a backup tarball. - Migrate your installation to a new cluster using the backup tarball as the data source.
Clean up
Because you installed Rancher and deployed your application cluster via Docker, you can clean up by stopping the Rancher
container and removing its contents from your local workstation, replacing [DOCKER_NAME] with the name of your Rancher
container.
docker stop [DOCKER_NAME] && docker rm [DOCKER_NAME]
You can also now clean up your Linux host, either by following the Rancher node cleanup doc or, in the case of a disposable VM, deleting it entirely.
Extend your Rancher and ngrok Kubernetes Operator integration
This combination of cluster management and secure, cloud-based public ingress can become a robust development environment for those still onboarding into the cloud native ecosystem or scale up to a multi-cluster production system—all with simpler and more secure ingress from ngrok.
Name-based virtual
hosting,
for example, allows you to deploy and manage any number of Kubernetes clusters and applications with Rancher and create
unique ngrok edge domains, like foo1.bar.com and foo2.bar.com, pointing to their respective services.
You can also configure the ngrok Kubernetes Operator with route modules, custom domains, or add edge security with OAuth, and more.
Learn more about the ngrok Kubernetes Operator, or contribute, by checking out the GitHub repository and the project-specific documentation.